Advancements in Privacy-Enhancing Technologies in Cryptocurrencies
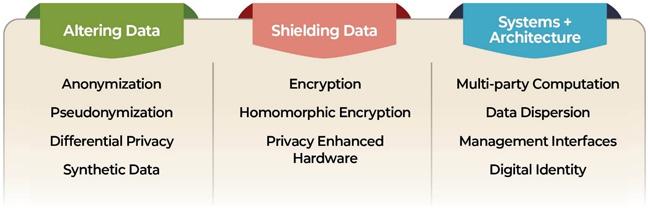
As the digital landscape evolves, the intersection of privacy and cryptocurrency has emerged as a critical focal point for both developers and users alike. With the proliferation of blockchain technology, concerns surrounding the anonymity of transactions and the protection of personal data have intensified. In response to these challenges, a wave of privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) has been developed, aiming to fortify user privacy while maintaining the integrity and transparency fundamental to blockchain systems. This article delves into the latest advancements in privacy-enhancing technologies within the cryptocurrency ecosystem, examining innovations such as zero-knowledge proofs, ring signatures, and secure multi-party computation. By providing a comprehensive overview of these sophisticated mechanisms, we aim to elucidate their significance in promoting confidentiality, enhancing user trust, and navigating the regulatory landscape that governs digital currencies today.
Table of Contents
- Emergence of Zero-Knowledge Proofs in Blockchain Transactions
- Enhancing User Anonymity through Decentralized Identity Solutions
- Robust Encryption Algorithms: A Key to Securing Cryptocurrency Wallets
- Regulatory Implications and Best Practices for Implementing Privacy Technologies
- In Retrospect
Emergence of Zero-Knowledge Proofs in Blockchain Transactions
The introduction of zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) marks a significant leap towards enhancing privacy in blockchain transactions. By allowing one party to prove to another that they know a value without revealing the value itself, ZKPs have the potential to create absolutely private transactions while maintaining network security. Their integration has enabled blockchain systems to move beyond the transparency paradigm, providing a shielded environment for users who are increasingly concerned about data privacy. With ZKPs, users can conduct transactions classified as confidential, where transaction amounts and recipient addresses remain hidden, preserving anonymity without compromising the integrity of the blockchain.
Several prominent blockchain projects have already adopted or are in the process of implementing ZKPs. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Privacy: Users can transact without disclosing sensitive information.
- Scalability: ZKPs can help reduce transaction data size, leading to faster processing times.
- Interoperability: They facilitate private transactions across different blockchain networks.
Notable Projects Utilizing ZKPs
| Project | Use of ZKPs |
|---|---|
| Zcash | Enables shielded transactions using zk-SNARKs |
| Ethereum 2.0 | Plans for ZK-rollups to improve scalability and privacy |
| Polygon | Utilizes ZKPs for scaling and privacy solutions |
Enhancing User Anonymity through Decentralized Identity Solutions
The emergence of decentralized identity solutions represents a significant shift towards enhancing user privacy in the realm of cryptocurrencies. Traditional identity systems often require individuals to share personal information and rely on centralized authorities, which heightens the risk of data breaches and identity theft. By contrast, decentralized identity systems leverage blockchain technology to enable users to control their own identity data. This empowers individuals to choose what information to share and with whom, ensuring that sensitive data remains private while still allowing for verification when necessary.
Key features of decentralized identity solutions include:
- Sovereignty: Users maintain ownership of their identities without dependence on a centralized authority.
- Privacy: Information is shared selectively, minimizing the data footprint in compliance with privacy regulations.
- Interoperability: Different platforms can interact seamlessly, facilitating a broader range of use cases.
- Security: Decentralization significantly reduces risks associated with single points of failure.
| Aspect | Decentralized Identity | Traditional Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Data Control | User-controlled | Central authority-controlled |
| Privacy | High | Variable |
| Risk of Breaches | Lower | Higher |
| Verification | Selective & Secure | Broad & Vulnerable |
Robust Encryption Algorithms: A Key to Securing Cryptocurrency Wallets
In the realm of cryptocurrency, where digital assets can be susceptible to theft and fraud, the implementation of robust encryption algorithms has become paramount. These algorithms serve as the backbone of security measures within cryptocurrency wallets, ensuring that users’ funds remain safe from unsolicited access. By utilizing advanced cryptographic techniques, such as elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) and SHA-256 hashing, wallets are able to provide a fortified barrier against external attacks. The significance of these algorithms lies not only in their ability to encrypt sensitive information, like private keys, but also in their role in maintaining the integrity of transactions on the blockchain.
Moreover, the integration of such encryption technologies often adheres to specific security protocols designed to thwart potential vulnerabilities. Key features include:
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adds an additional verification step to access wallets.
- Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) Wallets: Generate a new address for every transaction, enhancing privacy.
- Cold Storage Solutions: Keep the majority of funds offline, reducing exposure to online threats.
the development and application of encryption algorithms not only inspire confidence among cryptocurrency users but also pave the way for a secure ecosystem where privacy-enhancing technologies proliferate, ultimately fortifying the very vision of decentralized finance.
Regulatory Implications and Best Practices for Implementing Privacy Technologies
As the adoption of privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) in the cryptocurrency sector accelerates, several regulatory implications arise that stakeholders must navigate. Governments worldwide are increasingly focusing on consumer protection, anti-money laundering (AML), and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT) in an effort to regulate the cryptocurrency landscape. Due to these regulatory frameworks, developers and businesses must ensure that their use of PETs does not violate existing laws, which can vary substantially across jurisdictions. Organizations leveraging such technologies must take note of compliance requirements including:
- Developing a clear understanding of data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) relevant to their operations.
- Conducting regular audits to assess compliance with financial regulations.
- Implementing robust identity verification mechanisms while respect user anonymity.
To effectively integrate PETs while adhering to regulatory demands, enterprises should adopt best practices that promote transparency and accountability. These include creating comprehensive policies for the ethical use of privacy technologies and ensuring that stakeholders are consistently updated about regulatory changes. Establishing a feedback loop with regulators can also foster a productive dialogue around the innovative uses of PETs. Key recommendations in this regard are:
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Risk Assessment | Regularly evaluate potential risks associated with implementing PETs. |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Involve legal, compliance, and technical teams in decision-making processes. |
| Training & Awareness | Provide ongoing training for employees on best practices and compliance. |
In Retrospect
the evolution of privacy-enhancing technologies within the cryptocurrency landscape signifies a pivotal shift towards greater user autonomy and data protection. As we have explored, innovations such as zero-knowledge proofs, ring signatures, and advanced cryptographic protocols are not merely theoretical constructs; they are becoming integral components of secure blockchain implementations. These advancements not only address the pressing demands for privacy in an increasingly digital world but also elevate the potential for cryptocurrencies to gain wider acceptance in mainstream financial ecosystems.
However, the journey toward comprehensive privacy in cryptocurrencies is fraught with challenges, including regulatory scrutiny and the balance between anonymity and illicit activities. It is imperative for stakeholders—developers, users, and regulators alike—to engage in continuous dialogue to navigate these complexities. As we move forward, the ongoing development and integration of privacy-enhancing technologies will be crucial in shaping a more secure and private financial landscape, ensuring that the fundamental ethos of cryptocurrencies—user empowerment and financial sovereignty—remains intact. The future of digital finance will undoubtedly be influenced by how effectively these technologies evolve and are adopted in conjunction with a robust regulatory framework that fosters innovation while safeguarding against abuse.
