Unlocking Legal Clarity: Smart Contracts Transform Agreements
In an era where technology continues to reshape various facets of daily life, the legal landscape is undergoing a profound transformation with the advent of smart contracts. These self-executing agreements, embedded within blockchain technology, offer unprecedented transparency, efficiency, and security, challenging traditional notions of contractual relationships. As businesses and individuals alike seek alternatives to the complexity and ambiguity often associated with conventional contracts, smart contracts emerge as a compelling solution for unlocking legal clarity. This article explores the mechanics of smart contracts, their potential to revolutionize the way we approach agreements, and the implications for the future of legal practices in an increasingly digital world.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Smart Contracts and Their Legal Framework
- Key Benefits of Implementing Smart Contracts in Business Transactions
- Challenges and Considerations in the Adoption of Smart Contracts
- Future Trends: The Evolving Role of Smart Contracts in Legal Agreements
- The Way Forward
Understanding Smart Contracts and Their Legal Framework
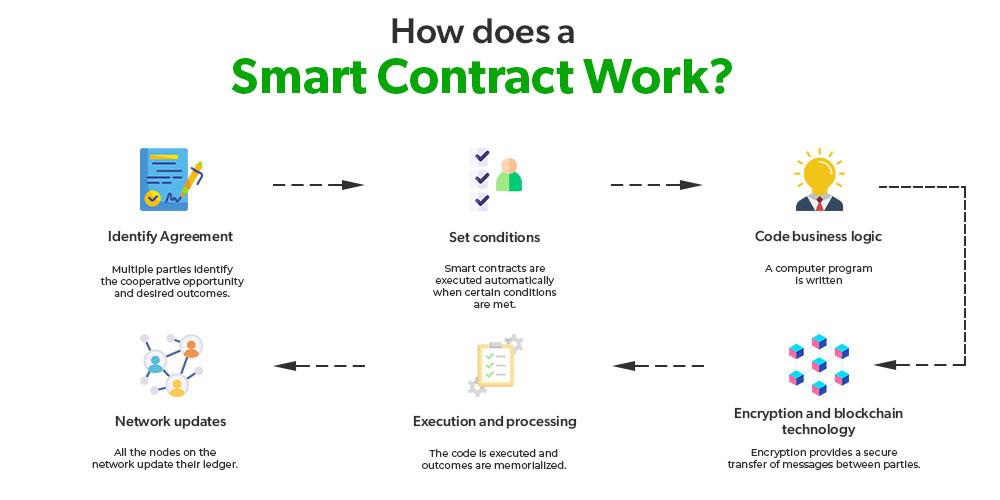
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, are rapidly reshaping how legal agreements are conceived and executed. Unlike traditional contracts, which require a third party to enforce and validate, smart contracts operate on blockchain technology, allowing them to execute automatically once predefined conditions are met. This autonomy enhances efficiency and reduces the potential for dispute. However, the legal framework surrounding these digital agreements remains complex and evolving. Key considerations include:
- Jurisdiction: Determining which legal system governs the smart contract.
- Enforceability: Examining how traditional contract law principles apply to automated agreements.
- Liability: Establishing who is accountable when a smart contract’s terms are violated.
To provide clarity, stakeholders must engage with legal professionals who understand both the technological and regulatory landscapes. Additionally, as adoption grows, regulatory bodies are beginning to draft guidelines to address intellectual property, consumer protection, and financial regulation in relation to smart contracts. This calls for a collaborative effort between technologists and lawmakers to prevent potential legal pitfalls. Below is a table summarizing the emerging issues and considerations:
| Issue | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Smart Contract Validity | Are digital signatures accepted? |
| Dispute Resolution | How will disputes be managed? |
| Compliance | Does the contract comply with local regulations? |
Key Benefits of Implementing Smart Contracts in Business Transactions
Smart contracts have the potential to revolutionize the way businesses conduct transactions by ensuring transparency and reducing the risk of disputes. These self-executing contracts are built on blockchain technology, allowing for the automatic enforcement of agreed terms without the need for intermediaries. The use of smart contracts can lead to significant cost savings through accelerated transaction times and reduced administrative overhead. Furthermore, they mitigate risks associated with fraud and misinterpretation, providing both parties with a clear and tamper-proof record of the agreement.
One of the standout advantages of smart contracts is their ability to enhance security and compliance. Through encryption and decentralized storage, sensitive transaction data is safeguarded from unauthorized access or tampering. Additionally, businesses can benefit from the incorporation of automated compliance checks, ensuring that each step of the transaction adheres to regulations and industry standards. This combination of security and automation creates a framework where trust is built inherently into the contract, fostering more robust business relationships. Below is a brief overview of the key benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces administrative costs by eliminating intermediaries. |
| Speed of Execution | Automates processes, leading to faster transaction finalization. |
| Security | Utilizes cryptographic techniques to ensure data integrity. |
| Transparency | All parties have access to the same data, minimizing disputes. |
Challenges and Considerations in the Adoption of Smart Contracts
The implementation of smart contracts brings forth a myriad of obstacles that organizations must navigate before fully embracing this groundbreaking technology. One significant challenge is the lack of legal recognition in many jurisdictions, which leaves the enforceability of smart contracts in a gray area. Many legal systems are still grappling with how to treat these self-executing agreements, and this uncertainty can deter businesses from adopting smart contracts. Additionally, the complexity of programming smart contracts necessitates a higher level of technical expertise, which may be a barrier for smaller organizations without dedicated resources. These firms may find it challenging to accurately encode all conditions and contingencies, risking potential vulnerabilities and misunderstandings in contractual intent.
Another critical consideration is the difficulty in dispute resolution. While smart contracts are designed to execute automatically without the need for intermediaries, this feature can complicate matters when conflicts arise. In traditional contracts, courts can interpret intentions, but smart contracts operate strictly according to coded instructions, leaving little room for flexibility in dispute resolution. Organizations must also address security vulnerabilities, as poorly coded smart contracts can be exploited, leading to financial loss and reputational damage. Moreover, the interoperability of smart contracts across different blockchain platforms remains an ongoing challenge, requiring further standardization and consensus to facilitate seamless integration. These considerations underline the need for a careful approach to smart contract adoption, balancing innovation with the fundamental principles of contractual law.
Future Trends: The Evolving Role of Smart Contracts in Legal Agreements
As technology continues to advance, smart contracts are becoming increasingly significant in the landscape of legal agreements. These self-executing contracts facilitate not only faster transactions but also enhance transparency and reliability in the execution of contractual obligations. By utilizing blockchain technology, smart contracts help eliminate the need for intermediaries, thereby reducing costs associated with contract enforcement. Legal professionals are recognizing the potential of this innovation to streamline processes, minimize disputes, and ensure timely compliance with contractual terms.
Future trends indicate a promising shift toward integration of smart contracts across various sectors. Key areas poised for transformation include:
- Real Estate Transactions: Smart contracts can automate the transfer of property titles and streamline mortgage processes.
- Supply Chain Management: They can provide real-time tracking and automate payment upon delivery, enhancing efficiency.
- Insurance Claims: By automating payouts based on predefined conditions, smart contracts can reduce fraud and speed up claims processing.
As legal ecosystems adapt to these changes, it is crucial for professionals to stay informed about the regulatory frameworks surrounding smart contracts to harness their full potential while ensuring legal compliance.
The Way Forward
As we stand on the cusp of a new era in contract law, the rise of smart contracts heralds a transformative shift in how agreements are formulated, executed, and enforced. By leveraging blockchain technology, these digital contracts promise to enhance transparency, reduce the potential for disputes, and streamline processes that have long been bogged down by bureaucratic complexities. However, as with any technological advancement, the path forward is not without its challenges. Legal professionals and stakeholders must navigate the evolving landscape of compliance, regulatory considerations, and the integration of traditional legal frameworks with digital innovations.
In unlocking legal clarity, smart contracts not only reshape our understanding of agreements but also compel us to reconsider the very principles that underlie trust and accountability in transactions. As the adoption of this technology continues to gain momentum, ongoing dialogue among legal experts, technologists, and policymakers will be crucial in ensuring that the benefits of smart contracts are realized while safeguarding the rights and interests of all parties involved. The future of contractual agreements is here, and its implications will resonate across industries, making it imperative for organizations to adapt and harness the power of smart contracts in their operational frameworks.




