Understanding Blockchain and Smart Contracts: Essential Insights
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the concepts of blockchain and smart contracts are gaining unprecedented attention, driving transformative changes across various industries. As organizations and individuals alike seek to harness the potential of these innovative technologies, a deeper understanding of their underlying principles and applications becomes essential. Blockchain, often synonymous with cryptocurrencies, extends far beyond mere financial transactions, offering a decentralized and secure method of recording and verifying information. Meanwhile, smart contracts, self-executing agreements with the terms of the contract directly written into code, are redefining traditional legal frameworks. This article aims to illuminate the intricacies of blockchain technology and smart contracts, providing essential insights for professionals, policymakers, and enthusiasts eager to navigate this complex landscape and leverage its potential for the future.
Table of Contents
- Exploring the Core Principles of Blockchain Technology
- The Mechanisms of Smart Contracts and Their Real-World Applications
- Navigating Legal and Security Considerations in Blockchain Deployment
- Best Practices for Implementing Blockchain Solutions in Business
- The Way Forward
Exploring the Core Principles of Blockchain Technology
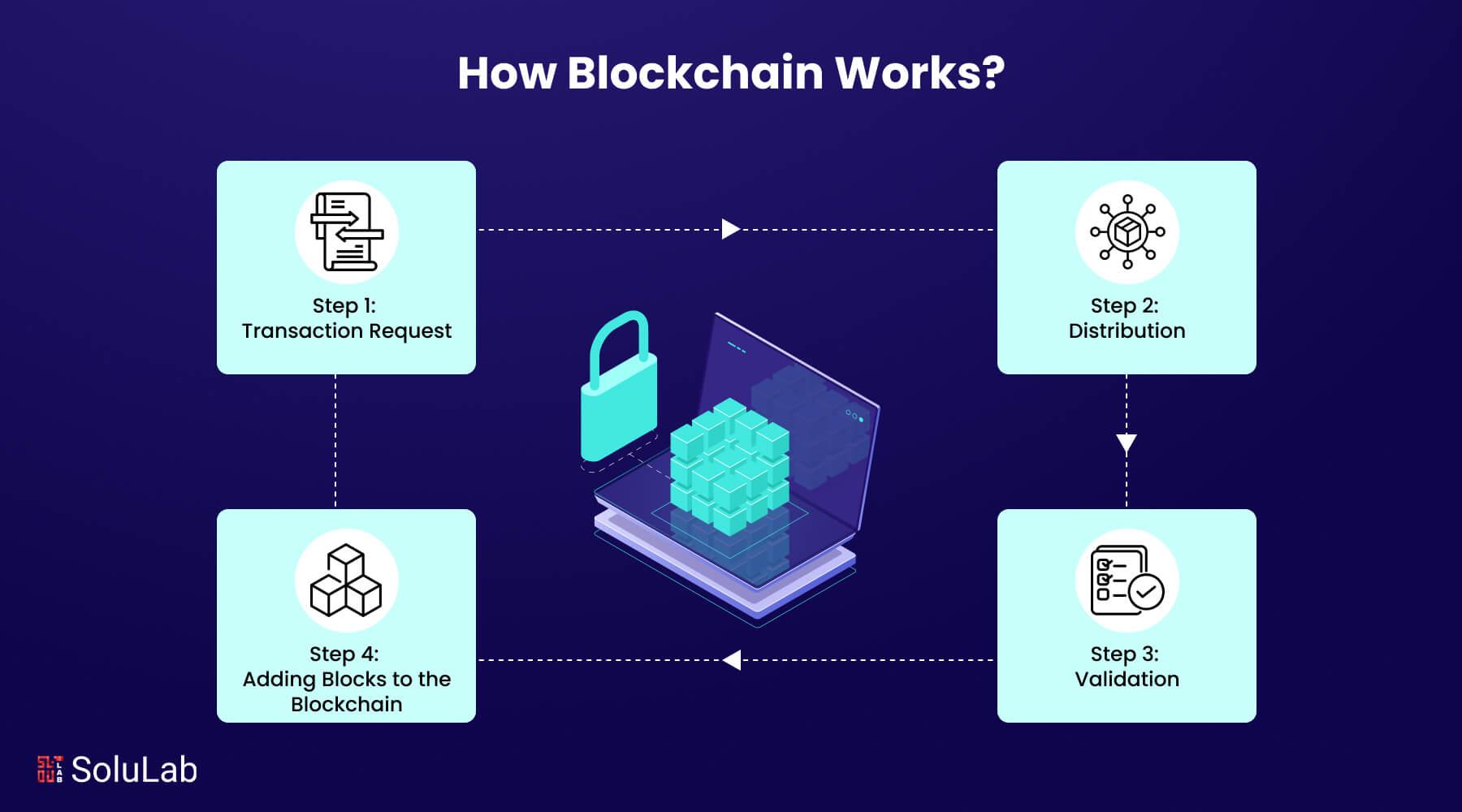
At the heart of blockchain technology lies a set of core principles that define its functionality and transformative potential. These principles include decentralization, which removes reliance on a centralized authority, thereby distributing power among users. This system enables enhanced security and resilience against tampering. Another essential principle is transparency; all transactions are recorded on a public ledger, allowing for real-time verification by anyone on the network. This level of openness fosters trust amongst participants and diminishes the risk of fraud.
Furthermore, immutability ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or erased, reinforcing the integrity of the data stored on the blockchain. Coupled with the principle of consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, blockchain remains secure and reliable, as these systems require validation from multiple parties before any transaction is approved. As a result, organizations can leverage blockchain to streamline processes and enhance compliance in sectors ranging from finance to supply chain management.
The Mechanisms of Smart Contracts and Their Real-World Applications
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms of the contract directly written into code. They operate on blockchain technology, ensuring that once deployed, they cannot be altered or tampered with. These contracts automatically enforce and execute their terms when predefined conditions are met. Key characteristics include:
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on the blockchain, providing a clear audit trail.
- Security: Information is encrypted and decentralized, reducing the risk of fraud.
- Efficiency: Automated processes reduce the need for intermediaries, expediting operations.
The real-world applications of smart contracts span various industries, demonstrating their versatility and potential for disruption. In finance, these contracts facilitate automated trading, enabling secure transactions without human intervention. In supply chain management, smart contracts track products from production to delivery, ensuring authenticity and compliance. Notable applications also include:
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Real Estate | Property transfers and lease agreements |
| Healthcare | Patient consent management and data sharing |
| Gaming | Ownership of in-game assets and rewards distribution |
Navigating Legal and Security Considerations in Blockchain Deployment
In the rapidly evolving landscape of blockchain technology, it’s paramount for organizations to consider the intricate legal implications surrounding their deployment strategies. A myriad of regulations can impact how blockchain solutions are developed, implemented, and utilized. Companies must be vigilant about compliance with local and international laws regarding data protection, privacy, and consumer rights. The decentralized nature of blockchain can challenge existing legal frameworks, necessitating a thorough understanding of jurisdictional issues and intellectual property rights concerning code and smart contracts. Organizations should prioritize engaging legal counsel specializing in technology to navigate these uncharted waters effectively.
Moreover, security considerations cannot be overstated when integrating blockchain solutions. While blockchain offers enhanced security features, potential vulnerabilities still exist. Key risks include smart contract bugs, user error, and cybersecurity threats. A comprehensive security strategy must encompass the following elements:
- Auditing Smart Contracts: Regular code reviews to identify and rectify vulnerabilities.
- Access Controls: Implementing strict protocols to manage permissions and user access.
- Data Encryption: Ensuring that sensitive data is encrypted both in transit and at rest.
Understanding and mitigating these risks will enable organizations to harness blockchain’s full potential while safeguarding their assets and reputation.
Best Practices for Implementing Blockchain Solutions in Business
When adopting blockchain technology, businesses should prioritize a comprehensive understanding of their unique operational needs and challenges. Conducting a thorough analysis is essential to determine how blockchain aligns with existing processes and whether it addresses specific pain points within the organization. In this context, it’s crucial to:
- Engage stakeholders from various departments to gain insights into their requirements.
- Assess current workflow inefficiencies that blockchain could resolve.
- Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of the implementation.
Moreover, selecting the right platform for blockchain implementation is vital for long-term success. Businesses must evaluate both public and private blockchain options based on their security, scalability, and governance needs. A structured approach involves:
- Researching existing blockchain frameworks and their suitability for specific use cases.
- Establishing partnerships with knowledgeable technology providers or consultants.
- Piloting the solution in a controlled environment to gauge performance before full-scale deployment.
The Way Forward
as we navigate the complexities of blockchain technology and smart contracts, it becomes increasingly clear that these innovations are not merely fleeting trends but foundational elements poised to reshape various industries. Their potential to enhance transparency, improve efficiency, and secure transactions offers significant advantages in an ever-evolving digital landscape. With ongoing developments and growing adoption across sectors, understanding the mechanisms and implications of blockchain and smart contracts is essential for stakeholders, businesses, and policymakers alike. As we stand on the brink of a new era in technology, the insights gleaned from this framework will be critical in informing decisions that drive innovation, regulatory measures, and economic growth. Embracing this knowledge will not only equip us to harness the benefits of these technologies but also prepare us to navigate the challenges that lie ahead.