Transitioning Landscapes: From Centralized to Decentralized Exchanges
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cryptocurrency and digital finance, the shift from centralized to decentralized exchanges (DEXs) marks a pivotal transformation in the way assets are traded and managed. Centralized exchanges, characterized by their reliance on trusted intermediaries to facilitate transactions, have dominated the market for years, offering users a streamlined experience alongside inherent vulnerabilities and regulatory challenges. However, the emergence of decentralized exchanges has ushered in an era of innovation, heralding a new paradigm defined by enhanced security, improved transparency, and the empowerment of users through self-custody of assets. This article delves into the technical underpinnings and implications of this transition, exploring the mechanisms that differentiate DEXs from their centralized counterparts, the benefits and challenges associated with their adoption, and the broader implications for the future of financial systems. As we navigate this complex landscape, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the forces driving this shift and the technological advancements that support it.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Shift: The Landscape of Centralized and Decentralized Exchanges
- Analyzing the Advantages: Benefits of Decentralization for Traders and Investors
- Technical Considerations: Security, Scalability, and User Experience in Decentralized Platforms
- Strategic Recommendations: Navigating the Transition to a Decentralized Exchange Ecosystem
- Key Takeaways
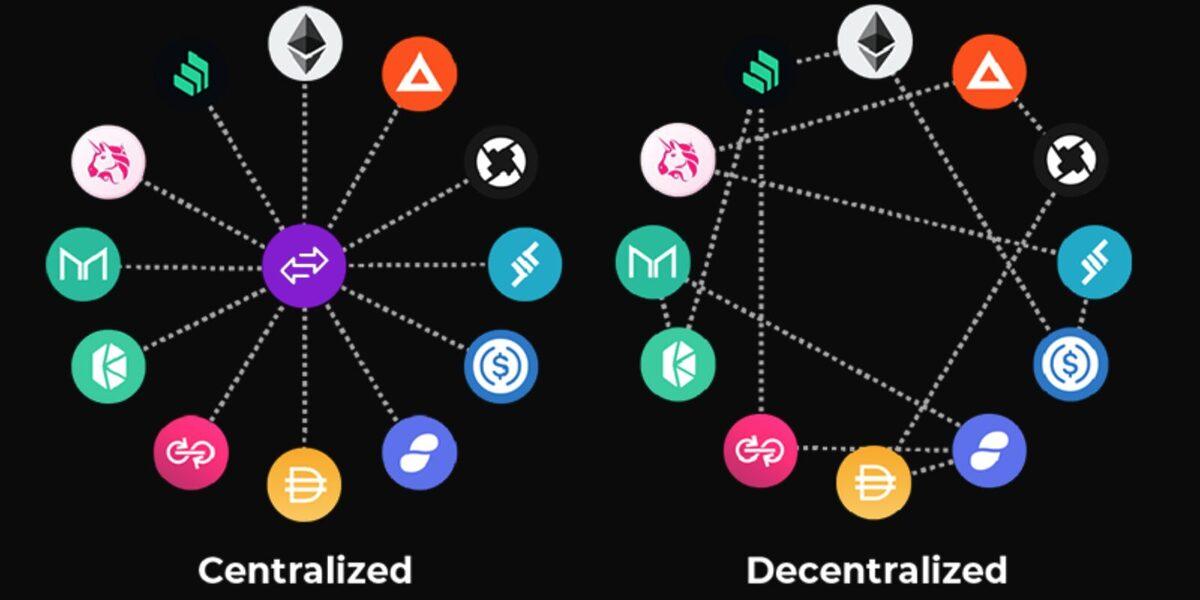
Understanding the Shift: The Landscape of Centralized and Decentralized Exchanges
The evolution of trading platforms has significantly altered the financial landscape, especially within the cryptocurrency realm. Centralized exchanges (CEX) traditionally serve as intermediaries that facilitate trading by providing services like order matching and customer support. These platforms are known for their user-friendly interfaces and extensive liquidity, making them attractive for new traders. However, they often come with risks such as potential hacks, regulatory issues, and losing control over personal assets. In contrast, decentralized exchanges (DEX) promote a peer-to-peer trading model that eliminates the need for intermediaries. This shift empowers users by allowing them to maintain full control over their funds and enhancing privacy, although it may require a steeper learning curve and can have lower liquidity in certain instances.
Moreover, the regulatory environment plays a crucial role in shaping the future of both exchange types. With increasing scrutiny from financial authorities worldwide, centralized exchanges are compelled to adopt stringent compliance measures, including Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) protocols. As a result, users might experience reduced anonymity and potentially face increased fees. Decentralized exchanges, on the other hand, often operate in a more lenient regulatory framework, harnessing blockchain technology to ensure transparency and security. Key differences between the two platforms are highlighted in the table below:
| Feature | Centralized Exchanges | Decentralized Exchanges |
|---|---|---|
| Control of Funds | Exchange holds user funds | User retains control |
| User Experience | Intuitive and user-friendly | Complexity may deter some users |
| Regulatory Compliance | Tightly regulated | Varies, often less regulation |
| Liquidity | Generally higher | Can be lower, depends on platform |
Analyzing the Advantages: Benefits of Decentralization for Traders and Investors
Decentralization in trading platforms is revolutionizing how traders and investors engage with markets by introducing significant benefits that directly enhance their trading experience. One of the primary advantages is increased control over funds, as users retain their private keys and do not need to rely on a central authority to manage their assets. This reduces the risk of hacks and mismanagement, fostering a safer environment for users. Furthermore, decentralized exchanges (DEXs) offer greater privacy since transactions occur on a peer-to-peer basis and do not require extensive personal information, contrasting sharply with the data collection practices of centralized platforms.
Another critical benefit lies in lower fees, as DEXs typically eliminate the overhead costs associated with maintaining a centralized server and its associated administrative expenses. This more economical model allows for more competitive trading rates, enabling users to keep a larger share of their profits. Additionally, market access becomes democratized; traders can participate in platforms that may have previously been restricted by geographical barriers or regulatory conditions. This leads to enhanced market liquidity and diversity, allowing investors to capitalize on a broader range of opportunities without the limitations of conventional exchange systems.
Technical Considerations: Security, Scalability, and User Experience in Decentralized Platforms
In the evolution of decentralized platforms, ensuring security remains a paramount consideration. Unlike centralized systems, where a single entity manages user data and funds, decentralized exchanges (DEXs) distribute this responsibility across the network, greatly minimizing points of failure. Key security features to implement include:
- Smart Contract Audits: Regular audits by third-party security firms to identify vulnerabilities.
- Multi-signature Wallets: Requiring multiple keys for transactions to reduce risks from unauthorized access.
- Decentralized Identity Verification: Using cryptography to ensure user anonymity while enhancing accountability.
Scalability presents another technical hurdle in DEX infrastructure. Unlike their centralized counterparts that can increase processing capacity through hardware upgrades, decentralized solutions must innovate at the protocol level to handle growing user bases and transaction volumes. Strategies to consider include:
- Layer 2 Solutions: Such as state channels and sidechains to alleviate congestion on the main blockchain.
- Sharding: Splitting the blockchain network into smaller chunks to improve transaction throughput.
- Optimized Algorithms: Utilizing more efficient consensus mechanisms to shorted block times and elevate user experiences.
Strategic Recommendations: Navigating the Transition to a Decentralized Exchange Ecosystem
As the market evolves towards decentralized exchanges (DEX), strategic initiatives are essential for stakeholders to thrive in this new landscape. Adapting to decentralized models will require investment in technology that enhances the user experience while ensuring security and privacy. Key actions include:
- Integrate liquidity solutions: Engage with liquidity aggregators to ensure competitive pricing and efficient transactions across multiple platforms.
- Enhance user education: Develop comprehensive guides and resources to educate users on the benefits and risks associated with decentralized trading.
- Implement robust security measures: Adopt advanced protocols such as multi-signature wallets and secure smart contracts to protect users from emerging threats.
Furthermore, collaborations among existing centralized exchanges and DEX platforms can foster a more harmonious transition. By leveraging shared technology and liquidity, these entities can create a hybrid trading environment that caters to various user demographics. Recommended strategies include:
| Strategy | Details |
|---|---|
| Cross-platform integrations | Facilitate interoperability between centralized and decentralized platforms to enhance trading options. |
| Regulatory compliance | Work with regulators to align decentralized models with existing legal frameworks, ensuring user protection. |
| Incentive programs | Launch user-friendly incentive schemes to promote trading on DEXs and retain users during the transition. |
Key Takeaways
the transition from centralized to decentralized exchanges represents a significant paradigm shift in the landscape of digital asset trading. As the cryptocurrency ecosystem continues to mature, the demand for greater transparency, security, and user autonomy has driven the evolution of decentralized platforms. This transition is not merely a technological advancement but a fundamental reconfiguration of the financial architecture that underpins trading systems.
As we look to the future, it is crucial for stakeholders—ranging from individual investors to institutional players—to understand the implications of this shift. Decentralized exchanges offer numerous advantages, including enhanced privacy, reduced custodial risk, and increased market resilience. However, they also present challenges such as liquidity concerns, user experience, and regulatory compliance.
The ongoing development of automated market makers (AMMs), layer two scaling solutions, and cross-chain interoperability will likely play pivotal roles in addressing these challenges. As innovations continue to emerge, it becomes imperative for participants in the crypto space to stay informed and adaptable. Ultimately, the success of decentralized exchanges will depend on a collaborative effort to enhance security, foster community trust, and promote regulatory frameworks that support innovation while ensuring user protection.
In this dynamic landscape, one thing remains clear: the migration towards decentralization signifies a transformative era in trading practices, paving the way for a more inclusive and resilient financial future.




