Navigating Blockchain: Balancing Data Privacy Challenges and Opportunities
In an era defined by digital transformation, blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force, promising unprecedented transparency and efficiency across various sectors. However, as organizations increasingly adopt decentralized systems, a complex landscape of data privacy challenges and opportunities has surfaced. The immutable nature of blockchain—the very feature that enhances its security and trustworthiness—also raises significant concerns regarding the protection of personal and sensitive information. As businesses and policymakers grapple with the dual imperative of harnessing blockchain’s potential while safeguarding individual privacy rights, navigating this intricate terrain demands a careful balance. This article delves into the critical intersections of blockchain innovation and data privacy, exploring the challenges that arise, the opportunities that can be seized, and the strategies necessary for fostering a secure and responsible blockchain ecosystem.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Data Privacy Landscape in Blockchain Technology
- Identifying Key Challenges in Data Security and Regulatory Compliance
- Exploring Blockchain Solutions for Enhanced Privacy and User Control
- Strategic Recommendations for Balancing Innovation and Data Protection
- To Wrap It Up
Understanding the Data Privacy Landscape in Blockchain Technology
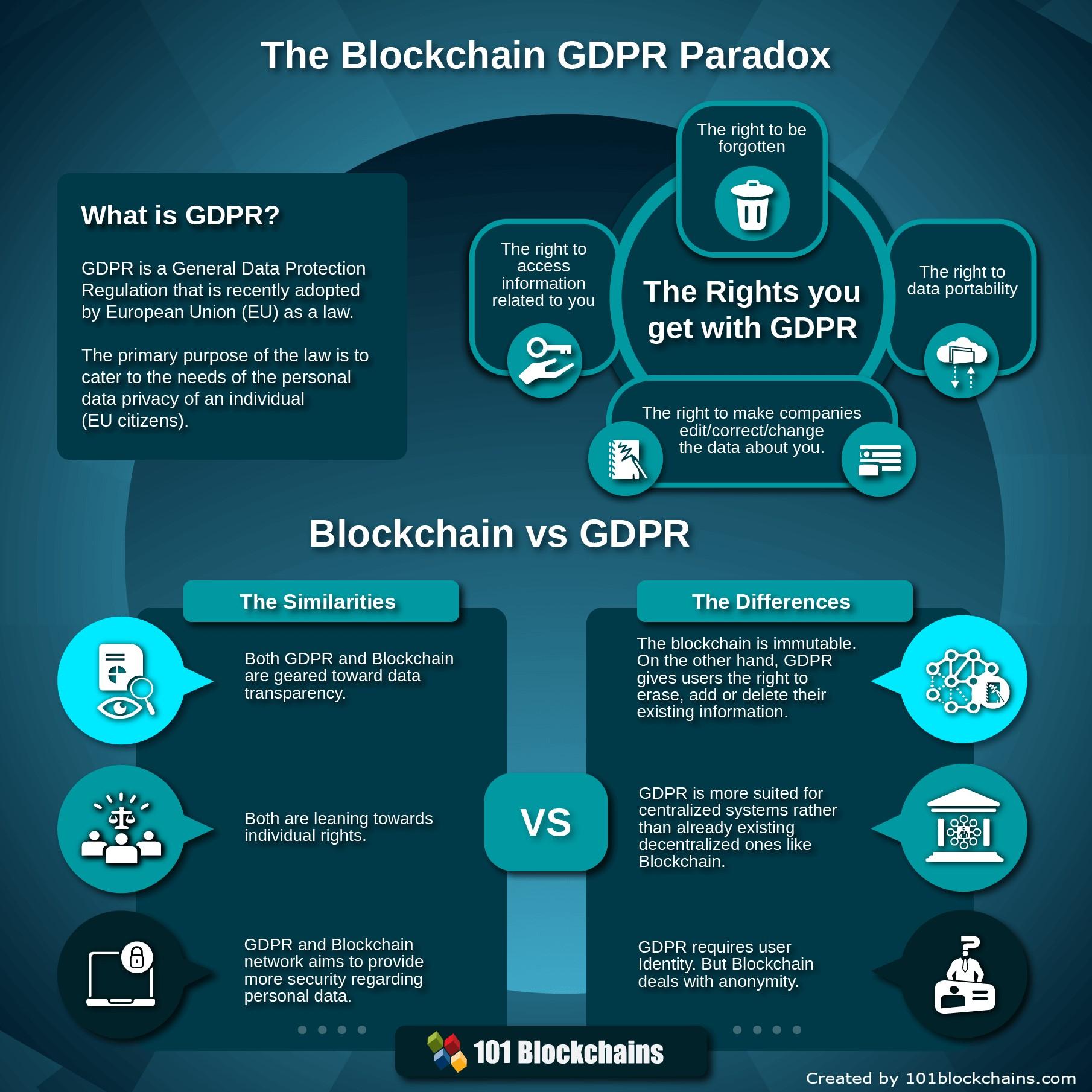
The intersection of blockchain technology and data privacy poses significant challenges that demand our attention. Traditional databases allow for strict data control and privacy measures, while blockchain, by design, promotes transparency and immutability. This dichotomy raises pertinent questions about data ownership and user privacy. Stakeholders must navigate issues such as:
- Data visibility: The public nature of certain blockchains exposes transaction details, potentially compromising user anonymity.
- Compliance challenges: The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other privacy laws create conflicts with unalterable blockchain records.
- Data breaches: While blockchain is often touted for its security, private keys and wallet addresses can still be susceptible to hacks.
On the flip side, blockchain technology has the potential to enhance data privacy through innovative solutions. Emerging techniques like zero-knowledge proofs and confidential transactions can enable private interactions within public ledgers. Additionally, decentralized identity protocols are being developed to empower users with more control over their personal data. Key opportunities in this space include:
- Self-sovereign identity: Users can manage their personal information without relying on a central authority.
- Data encryption: Advanced cryptographic measures can be implemented to secure sensitive data while maintaining transparency.
- Auditability: Blockchain allows for verifiable records without exposing granular user data, promoting accountability without compromising privacy.
Identifying Key Challenges in Data Security and Regulatory Compliance
As organizations increasingly adopt blockchain technology, they encounter significant hurdles in ensuring data security and meeting regulatory demands. The decentralized nature of blockchain can complicate traditional security protocols, exposing networks to unique vulnerabilities. Key challenges include:
- Data Management: Maintaining the integrity of data while ensuring its availability and confidentiality presents constant challenges.
- Regulatory Ambiguity: The fast-evolving landscape of blockchain regulations creates uncertainty, making compliance a moving target.
- Identity Verification: Establishing robust identity protocols to protect against fraud while preserving privacy is essential.
Furthermore, organizations must grapple with the implications of international regulations, which can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another. When developing blockchain solutions, regulatory compliance necessitates a comprehensive understanding of applicable laws to avoid costly penalties. The following table summarizes some important regulatory considerations:
| Regulation | Key Focus Areas | Geographic Scope |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Data Privacy and Protection | European Union |
| CCPA | Consumer Rights and Transparency | California, USA |
| FINRA | Securities Regulation | USA |
Addressing these challenges requires a nuanced approach that harmonizes technological innovation with rigorous compliance strategies. Stakeholders must prioritize education and collaboration to navigate this complex terrain, recognizing that failures in data security can have profound repercussions not just for organizations, but for consumers and society as a whole.
Exploring Blockchain Solutions for Enhanced Privacy and User Control
As concerns regarding data privacy continue to dominate the digital landscape, blockchain technology emerges as a pivotal solution offering enhanced privacy features. By decentralizing data storage, blockchain helps mitigate risks associated with centralized databases, such as data breaches and unauthorized access. Through the use of cryptography, blockchain enables users to control who has access to their information, ensuring that personal data is shared only when necessary. This paradigm shift promotes greater trust among users, as they gain more autonomy over their digital identities.
Various blockchain solutions are designed to cater to the needs of users seeking improved privacy measures. These solutions often integrate innovative features such as zero-knowledge proofs, which allow for transactions to be verified without revealing the underlying data, and privacy coins like Monero and Zcash, which provide unparalleled anonymity for their users. Below is a brief overview of key blockchain solutions that prioritize user privacy:
| Solution | Description | Privacy Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Monero | Privacy-focused cryptocurrency allowing confidential transactions. | Stealth addresses, Ring signatures |
| Zcash | Coin offering shielded transactions for enhanced privacy. | Zero-knowledge proofs |
| Ethereum with zk-SNARKs | Layer 2 solutions utilizing zero-knowledge proofs. | Transaction anonymity |
Strategic Recommendations for Balancing Innovation and Data Protection
To effectively navigate the intersection of innovation and data protection, organizations should prioritize the adoption of a risk-based approach. This entails evaluating the potential risks associated with blockchain technologies and their impact on personal data privacy. Key strategies include:
- Conducting Impact Assessments: Regularly evaluate how new blockchain applications may affect user data and privacy.
- Implementing Privacy-Enhancing Technologies: Explore cryptographic techniques that can safeguard data while leveraging blockchain’s capabilities.
- Balancing Transparency with Anonymity: Strive to maintain user transparency without compromising privacy, perhaps through pseudonymization methods.
Furthermore, organizations must foster a culture of compliance and education, ensuring all stakeholders are aware of the implications of data sharing on blockchain platforms. This can be supported by:
- Training Programs: Develop initiatives to educate employees on regulatory requirements related to data privacy.
- Collaborative Frameworks: Partner with legal experts and industry leaders to stay updated on best practices and compliance trends.
- Regular Audit Practices: Conduct periodic audits to ensure adherence to privacy policies and identify areas for improvement.
To Wrap It Up
navigating the complex landscape of blockchain technology presents both significant opportunities and formidable challenges, particularly in the realm of data privacy. As organizations leverage the strengths of blockchain—transparency, security, and decentralization—they must remain vigilant regarding the implications of data exposure and compliance with evolving privacy regulations. The delicate balance between harnessing the innovative potential of blockchain and safeguarding sensitive information will require ongoing dialogue among technologists, policymakers, and stakeholders. As the blockchain ecosystem continues to evolve, striking this balance will be crucial for fostering trust, protecting individual rights, and ensuring a sustainable future for digital transactions. Only by addressing these critical issues head-on can we unlock the true promise of blockchain technology while upholding the foundational principles of privacy and security in the digital age.




