Exploring Blockchain’s Role in Decentralized Storage Solutions
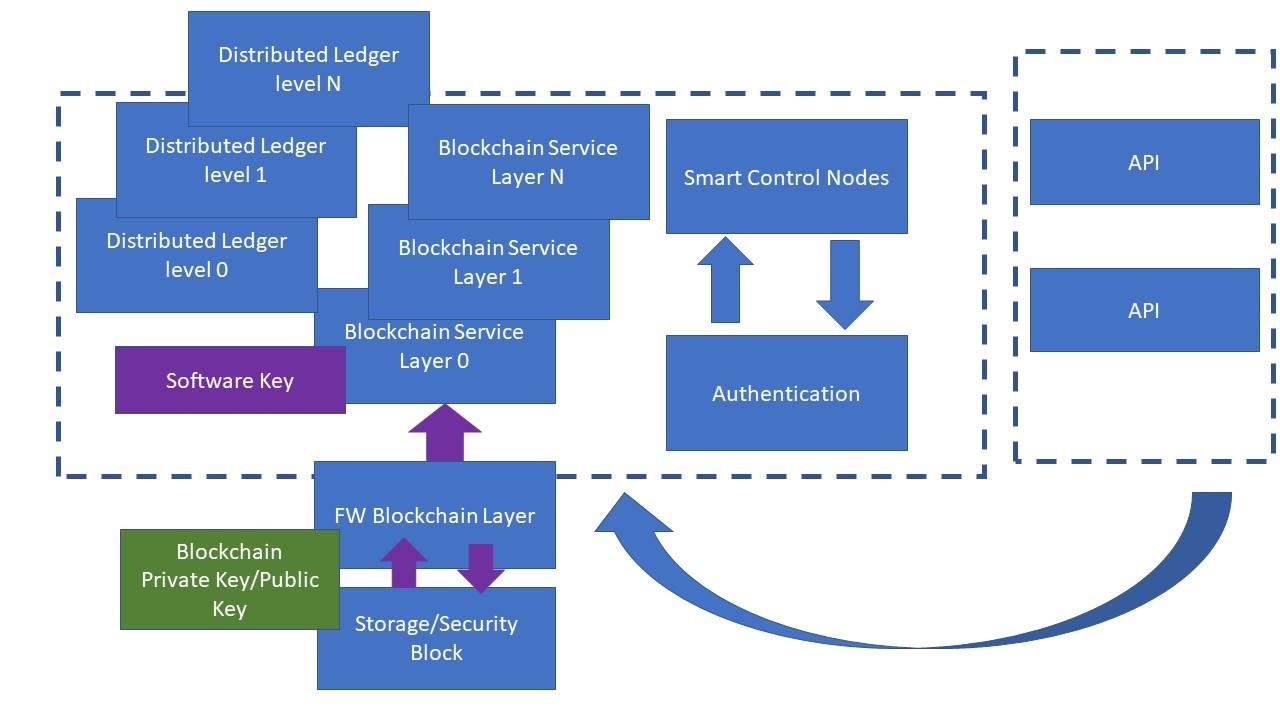
In recent years, the rapid evolution of blockchain technology has transcended its initial application in cryptocurrency, charting a new course for various sectors. One of the most compelling advancements is the rise of decentralized storage solutions, which promise to transform the way we manage data. As concerns about data security, privacy, and centralization grow, blockchain offers an innovative alternative that empowers users by distributing data across a network rather than relying on a single centralized authority. This article delves into the fundamental principles of blockchain-based storage systems, examines their potential advantages, and explores the challenges that lie ahead. By understanding the intersection of blockchain and decentralized storage, we gain insight into a future where data ownership and integrity are redefined.
Table of Contents
- Analyzing Blockchain Technologys Impact on Data Security and Privacy
- Evaluating the Efficiency of Decentralized Storage Models Compared to Traditional Solutions
- Identifying Key Players and Innovations in the Decentralized Storage Ecosystem
- Recommendations for Businesses Considering Blockchain-Based Storage Solutions
- The Way Forward
Analyzing Blockchain Technologys Impact on Data Security and Privacy
Blockchain technology stands as a formidable solution for enhancing data security and privacy, largely attributable to its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional data storage systems, where a central authority controls and manages data, blockchain distributes this responsibility across a network of nodes. This decentralization minimizes the risk of single-point failures and reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access. Key features that contribute to improved security include:
- Cryptographic Security: Data stored on a blockchain is encrypted, making unauthorized decryption exceedingly difficult.
- Immutable Records: Transactions on a blockchain cannot be altered once confirmed, ensuring the integrity of stored data.
- Decentralized Consensus: Multiple validation mechanisms must agree on transactions, limiting potential fraud.
Moreover, privacy is significantly enhanced through the use of advanced cryptographic techniques. For instance, zero-knowledge proofs and multi-party computation allow users to verify data without revealing the data itself. This transformative capability can empower users to maintain control over their personal information while still participating in various online activities. Below is a brief comparison highlighting traditional data storage methods versus blockchain storage:
| Aspect | Traditional Storage | Blockchain Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Centralized Authority | Decentralized Network |
| Data Integrity | Susceptible to Tampering | Immutable Records |
| Security | Vulnerable to Hacks | Cryptographically Secured |
| Privacy | Limited User Control | Enhanced User Privacy |
Evaluating the Efficiency of Decentralized Storage Models Compared to Traditional Solutions
The landscape of data storage is undergoing a transformation, as the decentralized storage models are emerging as formidable contenders to traditional solutions. While conventional storage often relies on centralized servers, which can be vulnerable to failures and breaches, decentralized systems distribute data across multiple nodes, enhancing security and reliability. Key advantages of decentralized models include:
- Improved data integrity: By achieving consensus across multiple parties, these models reduce the risk of data corruption.
- Enhanced privacy: Users have control over their data, significantly decreasing the chance of unauthorized access.
- Cost-effectiveness: Over time, decentralized storage can lower costs associated with maintenance and redundancy.
However, the efficiency of decentralized storage is often questioned in terms of speed and accessibility. Traditional solutions typically offer faster retrieval times due to their centralized architecture, which can streamline access. To better grasp the comparative statistics, the following table highlights important factors influencing both models:
| Factor | Decentralized Storage | Traditional Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Data Retrieval Speed | Slightly slower due to multiple nodes | Generally faster with centralized access |
| Security | High, due to distributed nature | Moderate, relies on centralized protections |
| Scalability | Highly scalable as new nodes can be added | Limited by hardware and infrastructure |
Identifying Key Players and Innovations in the Decentralized Storage Ecosystem
As decentralized storage solutions gain traction, several key players and innovative projects are at the forefront of this evolving ecosystem. Notable platforms are redefining how data is stored, accessed, and secured, leveraging blockchain technology to ensure transparency and decentralization. Some of the significant contributors include:
- Filecoin: A pioneering platform that incentivizes users to offer their unused hard drive space, creating a decentralized marketplace for storage.
- Storj: Utilizing a network of nodes for distributed storage, Storj enhances security and availability while reducing costs.
- Sia: A platform that splits files into smaller pieces, encrypts them, and stores them across the network, offering resilience against data loss.
Innovation within this sector is not limited to storage capacity; it also incorporates enhanced functionalities such as data integrity and retrieval speed. Noteworthy advancements include:
| Innovation | Description |
|---|---|
| Smart Contracts | Automated agreements for storage contracts, ensuring trust without intermediaries. |
| Redundancy Protocols | Techniques that ensure data is replicated across multiple nodes to prevent loss. |
This collaborative approach among diverse platforms not only strengthens the decentralized storage landscape but also pushes technological boundaries, fostering a robust environment for future innovation.
Recommendations for Businesses Considering Blockchain-Based Storage Solutions
Businesses exploring blockchain-based storage solutions should first conduct a comprehensive assessment of their operational needs and challenges. Identifying specific use cases can play a pivotal role in determining the right approach to implementation. Consider the following factors:
- Data Sensitivity: Determine the level of encryption and security required for the stored information.
- Capacity and Scalability: Evaluate the capacity needs, keeping scalability in mind for future growth.
- Compliance: Understand regulatory requirements in your industry and how blockchain storage can address them.
- Integration: Analyze how existing systems might integrate with blockchain technology.
Engaging with technology partners who specialize in blockchain solutions is advisable for businesses looking to leverage this technology effectively. Collaborating with experts can provide valuable insights that go beyond just technological implementation to include strategic advice tailored to your business model. Here are some benefits of such collaborations:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Expert Guidance | Access to specialized knowledge in blockchain applications. |
| Cost Efficiency | Identifying potential savings by optimizing storage solutions. |
| Risk Mitigation | Minimizing errors and ensuring compliance through best practices. |
The Way Forward
the exploration of blockchain technology reveals its significant potential to revolutionize storage solutions by promoting decentralization, security, and transparency. As traditional centralized systems face challenges related to data integrity, privacy breaches, and single points of failure, decentralized storage offers a promising alternative that empowers users and enhances data control. The collaborative efforts of innovators and developers in the blockchain space are paving the way for a new era of information management, where data ownership and reliability are paramount. As we move forward, it will be crucial for stakeholders—ranging from tech companies to regulatory bodies—to ensure that the evolution of decentralized storage aligns with best practices and ethical standards. The implications of this technology extend beyond mere storage, potentially reshaping industries and redefining our relationship with data in the digital age. As we continue to monitor this landscape, it is evident that blockchain’s role in decentralized storage will be a key focus for both researchers and practitioners in the years to come.




