Blockchain Revolution: A Path to Universal Banking Access
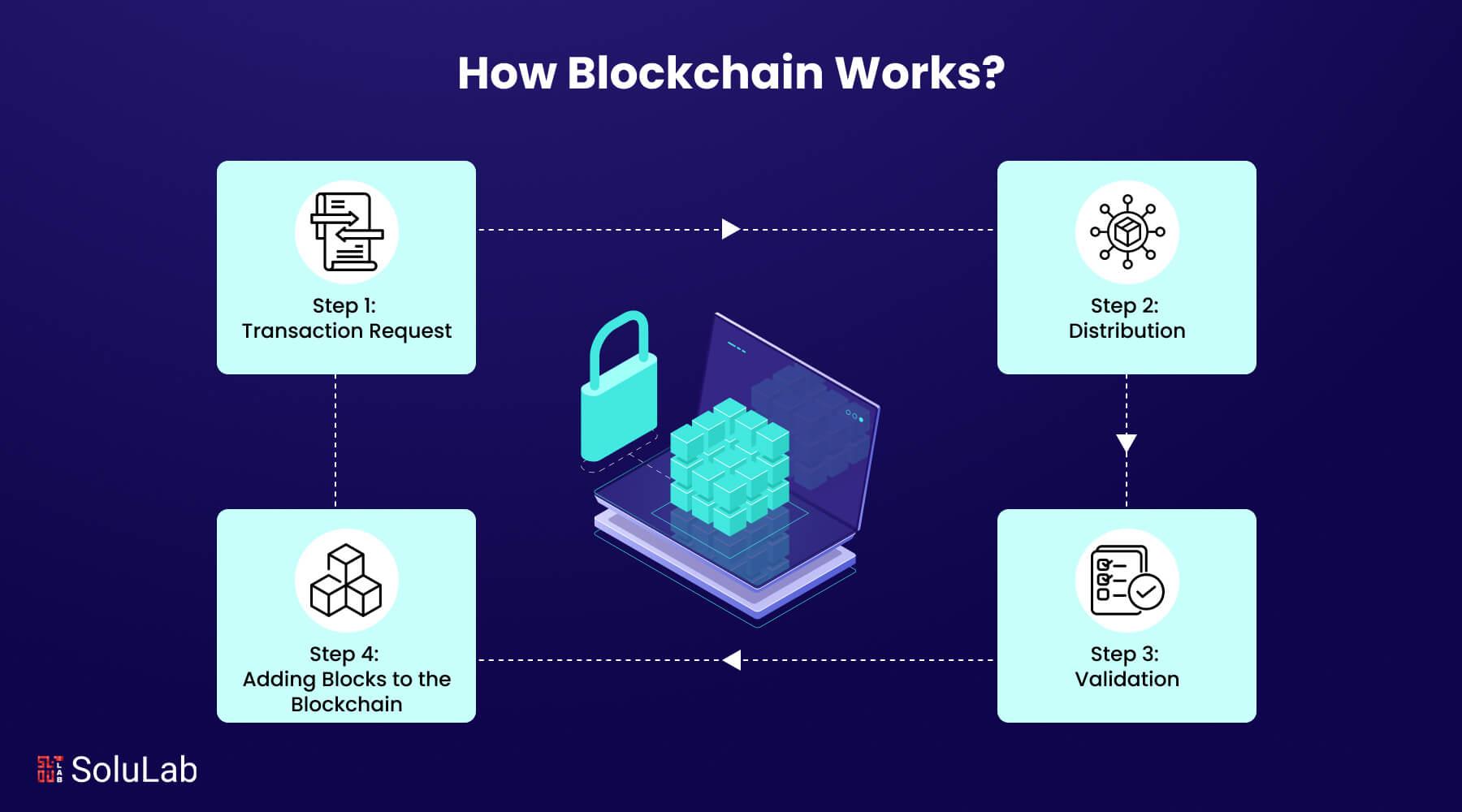
In an era marked by profound technological advancements, the concept of universal banking access emerges as a pivotal challenge and opportunity for global financial systems. As traditional banking institutions grapple with issues of inequality, inefficiency, and exclusivity, the blockchain revolution presents an innovative solution capable of reshaping the landscape of financial services. By decentralizing control and enhancing transparency, blockchain technology holds the potential to bridge the vast chasm between the banked and unbanked populations worldwide. In this article, we delve into how blockchain is not merely a trend but a transformative force that could redefine access to banking, empower underserved communities, and redefine the very fabric of financial transactions on a global scale. The promise of a more inclusive banking ecosystem is not just a vision—it is a path illuminated by the possibilities of blockchain.
Table of Contents
- The Role of Blockchain Technology in Democratizing Banking Services
- Examining the Impact of Decentralized Finance on Financial Inclusion
- Strategies for Policymakers to Leverage Blockchain for Universal Banking Access
- Challenges and Opportunities in Implementing Blockchain Solutions Globally
- In Conclusion
The Role of Blockchain Technology in Democratizing Banking Services
Blockchain technology has the potential to reshape the way banking services are accessed and delivered, addressing long-standing barriers of inclusion and accessibility. By decentralizing financial transactions, blockchain allows individuals, regardless of their geographical location or socio-economic background, to engage with banking services directly. This opens doors for marginalized populations, offering them the financial tools previously restricted to a privileged few. With blockchain, users can:
- Access low-cost remittance services, eliminating the high fees associated with traditional banking.
- Set up secure, digital wallets that enable safe storage of assets without the need for a bank account.
- Engage in peer-to-peer lending, facilitating direct financial support between individuals.
- Utilize decentralized finance (DeFi) applications that provide banking-like services without intermediaries.
The implementation of blockchain creates a transparent and secure environment for financial transactions, mitigating issues like fraud and bureaucracy. This is particularly crucial in regions where trust in traditional banking systems is low. The trustless, immutable nature of blockchain means that users can transact freely without needing to trust other parties or intermediaries. Additionally, with smart contracts, services can be automated, further reducing costs and increasing efficiency. The key benefits include:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced Costs | Lower fees for transactions and services compared to traditional banks. |
| Increased Speed | Real-time transactions without delays from intermediaries. |
| Financial Inclusion | Empowers unbanked populations to access financial services. |
| Enhanced Security | Immutability and encryption protect user data and assets. |
Examining the Impact of Decentralized Finance on Financial Inclusion
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is rapidly transforming the financial landscape by breaking down traditional barriers that have long hindered financial inclusion. Leveraging blockchain technology, DeFi platforms provide individuals, especially those in underbanked regions, equitable access to essential financial services. This movement introduces a new paradigm where users can engage in seamless transactions, earn interest on their assets, and access credit without the stringent requirements often imposed by conventional banks. As a result, the potential for a more inclusive financial ecosystem is within reach, motivating millions to participate in economic activities that were previously out of their grasp.
Key advantages of DeFi in promoting financial inclusion include:
- Lower Costs: DeFi eliminates intermediaries, significantly reducing transaction fees.
- Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection can access DeFi platforms, removing geographic limitations.
- Transparency: Smart contracts ensure that transactions are open and verifiable, fostering trust in the financial system.
- Empowerment: Users maintain control over their assets, reducing reliance on traditional banking infrastructures.
Recent data illustrates this shift; a
| Region | Percentage of Unbanked | DeFi Users Growth (2022-2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Sub-Saharan Africa | 66% | 200% |
| South Asia | 30% | 150% |
| Latin America | 50% | 100% |
report indicates a dramatic increase in DeFi user adoption in regions with high unbanked populations. This correlation underscores the potential of decentralized finance not only to enhance access but also to empower individuals economically. As DeFi solutions continue to evolve, they promise to play a crucial role in shaping a more inclusive financial future.
Strategies for Policymakers to Leverage Blockchain for Universal Banking Access
Policymakers can harness the transformative potential of blockchain technology to increase financial inclusion and universal banking access. By implementing a multi-stakeholder approach, they can foster collaboration between government institutions, private sector players, and non-profit organizations to develop innovative blockchain solutions. This cooperation can lead to creating a robust infrastructure that reduces transaction costs and enhances security, making banking services accessible to marginalized populations. Moreover, constructing permissive regulatory frameworks that prioritize innovation while maintaining consumer protection is crucial for encouraging fintech startups to enter the market and provide tailored solutions that meet the needs of underserved communities.
Investment in educational initiatives is paramount to ensure that both policymakers and potential users understand blockchain technology’s nuances. By conducting workshops, seminars, and producing resource materials, stakeholders can demystify blockchain and its applications in banking, ultimately expanding its adoption. Furthermore, leveraging public-private partnerships to pilot blockchain projects in regions with limited banking infrastructure will allow for real-world testing and data collection, informing future policy decisions. To centralize efforts, a dedicated task force could oversee these initiatives, focusing on actionable goals such as increasing account ownership rates and improving digital payment systems in rural areas.
Challenges and Opportunities in Implementing Blockchain Solutions Globally
Implementing blockchain solutions on a global scale presents a series of challenges that stakeholders must navigate carefully. Regulatory uncertainty remains one of the foremost obstacles, as governments struggle to develop comprehensive frameworks that both encourage innovation and safeguard public interests. Without clear guidelines, organizations may face legal hurdles that complicate the adoption of blockchain technology. Additionally, interoperability issues arise when different blockchain platforms cannot communicate with one another, limiting the effectiveness of solutions designed to unify and streamline banking access globally. The digital divide further complicates matters, as regions with limited internet infrastructure may struggle to leverage the benefits of blockchain, thus perpetuating existing economic disparities.
However, these challenges also present significant opportunities for innovation and collaboration. By investing in educational initiatives, organizations can raise awareness about blockchain technology and foster a skilled workforce capable of developing and managing decentralized solutions. Partnerships between private companies and governments can lead to the creation of regulatory frameworks that balance innovation with oversight, stimulating responsible growth within the industry. Furthermore, advances in scalability solutions, such as Layer 2 technologies, could bridge the gap between existing systems and distributed networks, making blockchain technology more accessible and efficient. As these barriers are addressed, the vision of universal banking access could become not only achievable but imminent.
In Conclusion
the blockchain revolution stands as a transformative force poised to reshape the landscape of global finance, particularly in the realm of banking access. By dismantling traditional barriers and fostering inclusivity, blockchain technology offers unprecedented opportunities for the unbanked and underbanked populations across the world. As stakeholders from governments to tech innovators engage in collaboration, the potential for a more equitable financial system becomes increasingly attainable. However, it is crucial to navigate the challenges accompanying this evolution, including regulatory frameworks, security concerns, and digital literacy. As we stand on the brink of this new era, the commitment to leveraging blockchain’s capabilities for universal banking access will be paramount in building a more inclusive and resilient financial future for all. The journey ahead promises to be complex, yet with careful stewardship, it holds the potential to bring banking services into the hands of millions who have been marginalized for far too long.
